This article is a continuation of my embryology series if you have not read about blastulation, I recommend you reading it before reading this article and you can do that by reading my article. If you are done with that article then you are good to go.
So we left the last article on blastocyst, before moving further in embryology part, I want to tell you some things that will ease the process of understanding the super detailed process of embryology
So what was the product after blastulation – it was blastocyst right, well yes but remember the term “Blastocyst” is used only for mammals and term -“Blastula ” is used for lower animals, although both are same, the name is different due to their appearance. When scientist noticed the end structure of blastulation in case of mammals, it appeared like a cyst, so they just called it blastocyst instead of a blastula
So what were the cells in the blastocyst , you remember ?
There were two masses of cells :-
1)-Outer cell mass.(Trophoblast)
2)-Inner cell mass.
See image attached below:-
Now I mentioned these cells again for a reason. I mentioned them again because I want you to note two things before moving further
- Outer cell mass or Trophoblast will form “PLACENTA” in future. (note it )
- Inner cell mass will form the future “EMBRYO”, that’s why they are also known as -“Embryoblast cells”
See the image below :-

So that means majorly now two things will go on :-
Outer cell mass or trophoblast cell will undergo some process and will form the placenta and Inner cell mass will undergo some processes and they will form the future foetus.
I hope, that now you are clear with a idea that which cell will form which part.
just for a quick review:-
- Outer cell mass or Trophoblast —-> placenta
- Inner cell mass or Embryoblast —–>Future foetus
NOTE – Foetus and embryo are two different things on the basis of their gestational age (for how much time they are inside the mother womb) Embryo means the structure of the early stage, while the Foetus refers to an advanced structure which has crossed 11 weeks of gestation in mother womb.
Now as we have two types of cells in the blastocyst that means majorly two processes will go on in this week – one is placenta development and another one is the development of an embryo from embryoblast cells
Now before starting those process, I want you to focus on the location of the blastocyst, Yeah think where actually blastocyst really is, in the mother womb?
let me tell you where the blastocyst actually is ?
Let’s dive in to female reproductive tract , super fast ——
look at the diagram below:-
note the marked point , carefully observe the whole diagram now.
Noticed something ? , well let’s match my observation and your observation , You must have observed that blastocyst is not embedded in endometrium lining of uterus , if you did not noticed it , look at the diagram again, why i am stressing so much on these point is because i want you to remember that – “Early Blatocyst is present in uterine cavity it is not implanted , yes it is not yet implanted in endometrium , it is to be implanted but as of now it is present i the uterine cavity
Let’s make the concept more clear , look at the below diagram also :-
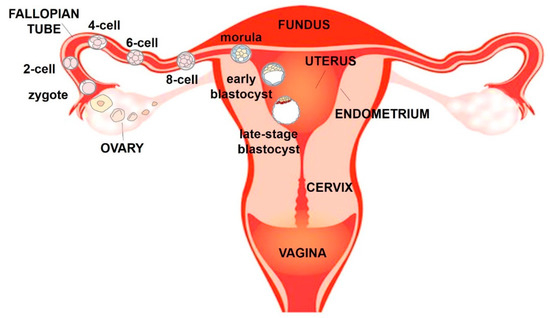
Observe the above diagram, what I want you to notice is the difference between an early blastocyst and late-stage blastocyst, as a good student you must know that early Blastocyst is not implanted but the late-stage blastocyst is implanted in Endometrium lining of the uterus,
Note:-
- About 7-14 days after fertilization, implantation will occur—the fertilized egg will attach itself to the lining of your uterus. About one-third of women will have some bleeding when implantation takes place.
- Women are now considered to be pregnant.
Now our area of interest is how does implantation take place? and why there occurs bleeding in 1/3rd of women?
Well let’s find out and learn together –
outer cell mass or trophoblast when come in contact with endometrium they secretes some perforating chemicals which help the early blastocyst to pierce the endometrium lining and getting implanted in it and during that perforation endometrium is damaged that result in slight bleeding in some females
So that’s how a late blastocyst get implanted in endometrium . let’s see this event diagramatically.

so now the Late blastocyst is in the endometrium and is implanted and female is said to be pregnant.
It was easy , isn’t it ? , Well I missed a very important point and I will tell that point now , as I want you to remember that point as a good student .
Note:-Blastocyst was covered by zona pellucida so if we assume trophoblast(outer cell mass) secretes some substances that help the blastocyst to pierce the endometrium then what happened to zona pellucida ? ? Does those substances which were designed to pierce the endometrium also pierced the zona peelucida ? Actually Before the secretion of those chemicals by trophoblast, Embryo undegoes one Wondrous event called :- “Hatching ” Hatching is simply defined as shedding off the zona pellucida layer by blastocyst . so after hatching blastocyst is only left with trophoblast and embryoblast cells and no zona pellucida
Image showing hatching :-

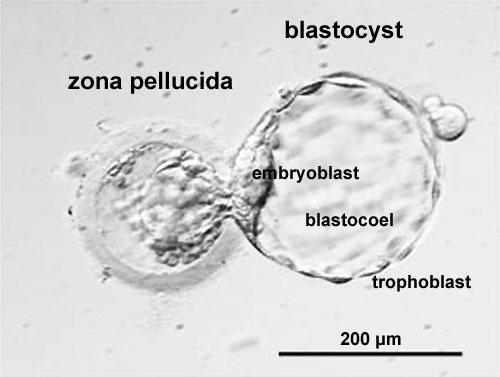
So after hatching the blastocyst enters the endometrium (Remember the hatching point as many students are completely unaware of such wondrous event )
Now blastocyst after entering in endometrium needs nutrition to further develop so the blastocyst need to develop connection with the mother blood vessel in endometrium and blastocyst does it by developing a “placenta” and the process of development of placenta is – “Placentation”
Now as the blastocyst undergoes placentation to develop connection for further nutrition support , the embryoblast use the remaning nutrituous content from the blastocoel to further grow and forming two layers and for going in an another wondrous event -“Gastrulation”
Now let’s be serious as two major process will go on from here
- Dvelopment of placenta
- Dvelopment of two layers of cells (Bilaminar disc) from inner cell mass
I will be talk about placentation in another article as it is such an elaborative process , trust me guys and explaining it in just written form is an another challenge for me , I will talk about it later
I will talk about the fate and development of Embryoblast in another article too as it is also an super elaborative process.
I want you to notice an another interesting process in this article before moving on to the develoment of placenta
Let’s discuss about the fixation of blastocyst in endometrium , secretion of HCG, fate of trophoblast.
Fate of trophoblast
as I already told you that trophoblast is responsible for the development of placenta , well yeah it forms the future placenta but I want to discuss some initial step of placentation as they will explain to you about the fixation of blastocyst in endometrium and HCG secretion.
So the trophoblast now start dividing and it divides to form cell linings which just spread inside the endometrium , I want you to be attentive now ,Iam repeating again _”Trophoblast cells start proliferationg and dividing on a very high speed and they start spreading across the whole endometrium , just similar to how roots spread inside the soil
Look at the diagram below :-

As you can see in above diagram trophoblast are just spreading in endomterium just like root spreads in the soil
Now trophoblast differentiate in two different cells – One is synctiotrophoblast and another is cytotrophoblast
BE ATTENTIVE NOW ! , See, what happens is . that some of the cells of trophoblast which were spreading in endometrium strart dissovling their cell membrane with another cells , in short cells start fusing with one other forming a lump of cytoplasm with a lot of nuclei floating inside it , it just like a “boondi raita” , imagine the boondi as nucleus of fused cells and raita as cytoplasm of the cell which has undergone fusion.

I know the examples looks funny but believe me I did not find any another easy way of explaining it and now that lumpo of cytoplasm get surrounded by a common cell membrane and that created a synctium (Synctium is a multinucleated structure formed by the fusion of cells) but remember one thing not all the cells have undergone fusion , only some of the cells undego fusion to form synctium while other trophoblast cells just stay on their location as outercovering
Remember I told you that trophoblast form two type of cells , now let’s learn about them . The cells which are destined to undergone fusion to form synctium are known as ” Synctiotrophoblast “ while on the other hand, cells which are not destined to undergo the fusion and remain as they were are known as –“Cytotrophoblast”
So long stroy short Trophoblast or outer cell mass will form and diffentiate to two type of cells – Synctiotrophoblast (which will form the synctium) and Cytotrophoblast (which will occupy there space as outer layer and do not undergo fusion
it looks like this :-

More refined image :-
Note :- Pay attention toward some things now :-
- Cytotrphoblast may be present inside the synctium structure may be outside of them or may be just as lining of whole blastocyst
- Inner cell mass faces away from the endomterium lining , Note it down the inner cell mass is located away from the point where the blastocyst has just entered
Histology link
Histology image of syctio and cytotrophoblast

So this synctium just fixes the position of the developing embryo inside the endometrium , yes the meshwork help hold the developing embryo its location
Now what if endometrium get shed ? as you might be knowing endometrium is not an stable lining instead it is the one of the most unstable lining and we need to maintain this endometrium as now blastocyst has just fixed itself inside of it
As you might be knowing Corpus luetum maintains the endometrium lining and if the corpus luetum is not maintained than endometrium will be shed off and an Hormone named HCG also known as pregnancy hormone maintains the corpus luetum thus indirecty maintaining the endometrium lining and this hormone is secreted by Synctiotrophoblast in initial stage , so synctiotrophoblast make sure that endometrium is maintained by releasing the HCG , later the HCG is secreted by placenta (obviously you know that trophoblast will be forming the placenta)
Linking concepts
Well I will discuss placentation in another article but i was unable to stop myself to tell you an interesting concept that will help you in understanding the placentation. let me tell you that there are many maternal blood vessel in endometrium and as synctiotrophoblast is developed , it start to grow more in length chasing the mother blood vessel just like roots chase the water in soil and guess what will happen when the synctiotrophoblast will meet the maternal blood vessel – it will form the placenta (although the process is super elaborative but now you have an basic idea what will go on next) see in the diagram below point no. 6 shows maternal vessel and synctiotrophoblast is increasing in length to reach to it .

Thanks for reading it , enjoy learning
Signing off from my side
Bhavesh saini.


Comments
Post a Comment